A recent study reveals that Kallistatin levels rise after weight loss, offering potential new treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes through its positive effects on metabolism and hepatic insulin sensitivity.
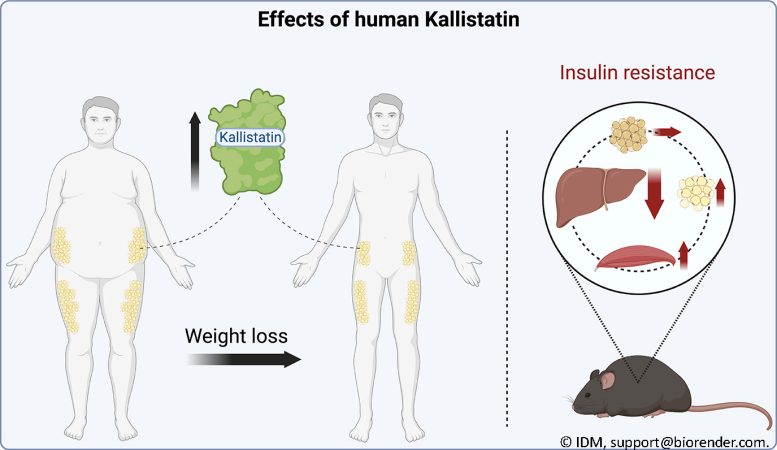
Following weight loss, individuals previously classified as overweight or obese exhibit increased levels of the protein Kallistatin in their subcutaneous white adipose tissue, according to a recent study conducted by researchers at the DZD.
In addition, Kallistatin improves metabolism and could open up new therapeutic options for people with obesity and type 2 diabetes in the future. The results have now been published in Molecular Metabolism.
An increasing number of people are developing type 2 diabetes and obesity. These are highly complex and multifaceted diseases. In order to treat them sustainably, new approaches to therapy are needed. Clinical studies on humans have shown that heavily overweight individuals produce less Kallistatin. Kallistatin is a protein that has various effects in the body. Among other things, it is involved in counteracting inflammation and healing wounds.
Expression of the protein Kallistatin increases after weight reduction. In mice, it improves hepatic insulin sensitivity. Credit: IDM, [email protected]
The role that Kallistatin plays in glucose metabolism and its potential suitability as a therapeutic target are currently being investigated by researchers from the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), the Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases (IDM) of Helmholtz Munich at the Eberhard-Karls-University of Tübingen, and the Department of Diabetology, Endocrinology and Nephrology at the University Hospital Tübingen.
Kallistatin Expression Increases After Weight Loss
To this end, they measured Kallistatin expression in subcutaneous white adipose tissue in 47 individuals with overweight to obesity before and after weight loss. The result: Kallistatin expression increases after weight loss.
Kallistatin Improves Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity
Additionally, the researchers examined the effect of the protein in an animal model. In the process, they observed that human Kallistatin improves hepatic insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice.
“Our results suggest that Kallistatin may be an interesting, yet challenging, therapeutic target for people with obesity and insulin resistance,” says lead author Leontine Sandforth. “Because Kallistatin has insulin-sensitizing effects in the liver, it should be investigated as a potential liver-specific target for emulating the beneficial effects of weight loss and potentially treating type 2 diabetes and obesity,” adds last author Prof. Andreas Birkenfeld.
Reference: “Role of human Kallistatin in glucose and energy homeostasis in mice” by Leontine Sandforth, Sebastian Brachs, Julia Reinke, Diana Willmes, Gencer Sancar, Judith Seigner, David Juarez-Lopez, Arvid Sandforth, Jeffrey D. McBride, Jian-Xing Ma, Sven Haufe, Jens Jordan and Andreas L. Birkenfeld, 29 February 2024, Molecular Metabolism.
DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101905





