The Series 1 Lander was optimized for light weight, small size and reliability. Although the lander did not complete a soft landing, the cause has been identified and improvements are being incorporated into Mission 2 and Mission 3. Credit: ispace
The HAKUTO-R Mission 1 lunar lander, launched by ispace in December 2022, failed to land safely on the Moon. In April 2023, NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter detected unusual surface changes and debris near the intended landing site, suggesting potential remnants of the unsuccessful landing. Further analysis is planned to verify these findings.
The ispace HAKUTO-R Mission 1 lunar lander was launched on December 11, 2022, a privately funded spacecraft planned to land on the lunar surface. After a several-month journey to the Moon, the spacecraft started a controlled descent to the surface to land near Atlas crater. The ispace team announced the following day that an anomaly occurred, and the HAKUTO-R Mission 1 lunar lander had not safely touched down on the surface.

HAKUTO-R Mission 1 lunar lander site, as seen by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) on April 26, 2023, the day after the attempted landing. The scale bar is 100 m across. LROC NAC image M1437131607R. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Arizona State University

LROC Narrow Angle Camera mosaic of the HAKUTO-R Mission 1 lunar lander site made from the following image pairs: M1437138630L/R, 1437131607L/R, M1437124584L/R, 1437117561L/R, M1437110537L/R. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Arizona State University
On April 26, 2023, NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) spacecraft acquired 10 images around the landing site with its Narrow Angle Cameras. The images covered a region roughly 40 km by 45 km (about 25 miles by 28 miles). Using an image acquired before the landing attempt, the LRO Camera science team began searching for the lander.
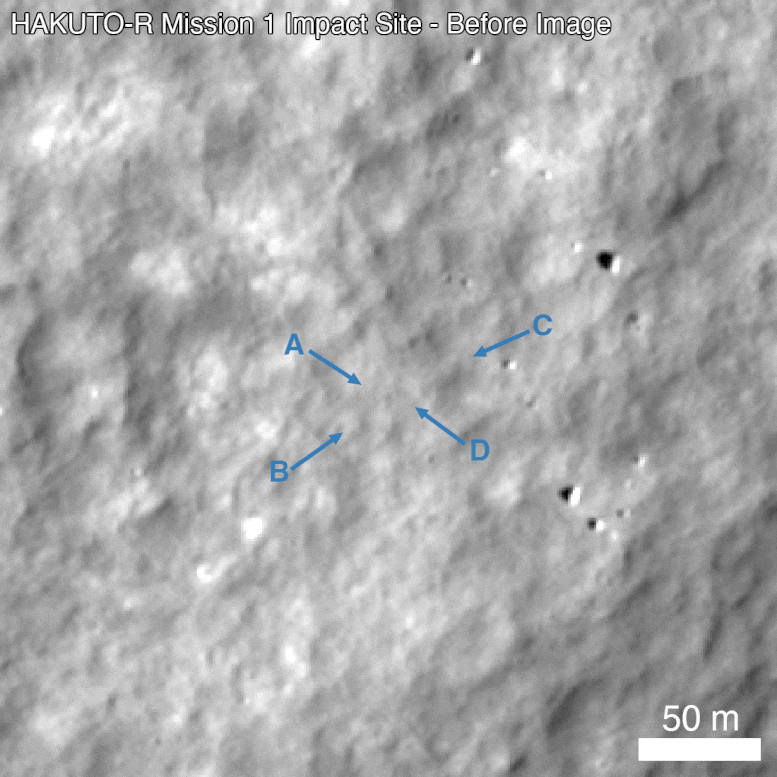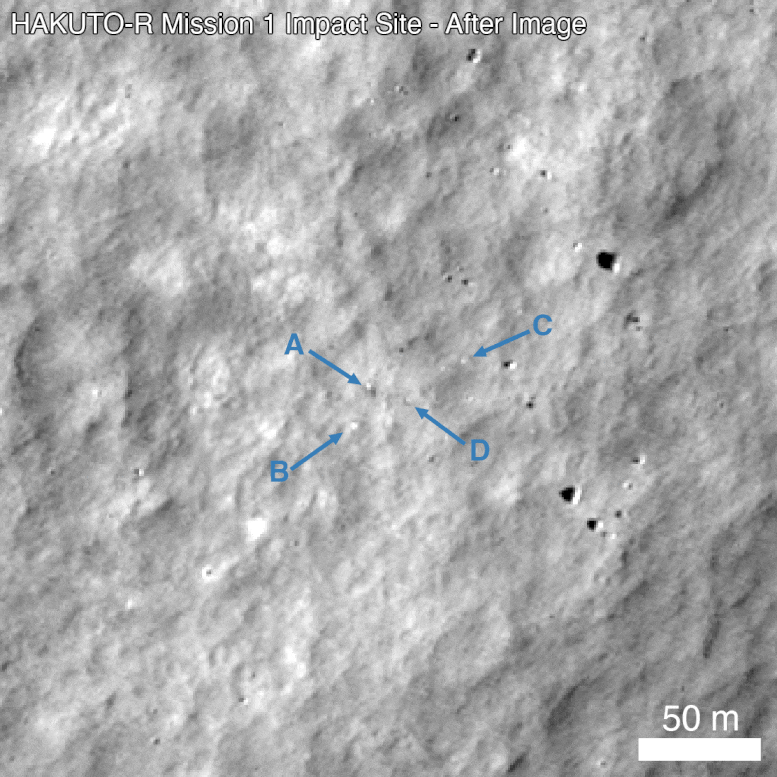
Before (M192675639R) and after (M1437131607R) comparison of the impact site. Arrow A points to a prominent surface change with higher reflectance in the upper left and lower reflectance in the lower right (opposite of nearby surface rocks along the right side of the frame). Arrows B, C, and D point to other changes around the impact site. The scale bar in the lower right is 50m across. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Arizona State University
From the temporal image pair, the LRO Camera team identified an unusual surface change near the nominal landing site. The image shows at least four prominent pieces of debris and several small changes (47.581 degrees North latitude, 44.094 degrees East longitude). The central feature in the image above shows several bright pixels in the upper left and several dark pixels in the lower right. This is the opposite of nearby boulders, suggesting that this could be a small crater or different parts of the lander body. This site will be further analyzed over the coming months as LRO has the opportunity to make additional observations of the site under various lighting conditions and viewing angles.

Ratio image created by dividing the after (M1437131607R) and before (M192675639R) images. The impact created an area of higher reflectance, approximately 60-80 m across. The scale bar in the lower right is 50m across. Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Arizona State University
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter is managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Launched on June 18, 2009, LRO has collected a treasure trove of data with its seven powerful instruments, making an invaluable contribution to our knowledge about the Moon.




