Quantum computers, utilizing versatile qubits, are at the forefront of solving complex optimization problems like the traveling salesman dilemma, traditionally plagued by computational inefficiency. Through rigorous mathematical analysis, researchers have demonstrated that quantum computing can fundamentally transform problem-solving, offering a more efficient polynomial increase in computation time compared to classical methods and yielding superior solutions.
The traveling salesman problem is considered a prime example of a combinatorial optimization problem. Now a Berlin team led by theoretical physicist Prof. Dr. Jens Eisert of Freie Universität Berlin and HZB has shown that a certain class of such problems can actually be solved better and much faster with quantum computers than with conventional methods.
Quantum computers use so-called qubits, which are not either zero or one as in conventional logic circuits, but can take on any value in between. These qubits are realized by highly cooled atoms, ions, or superconducting circuits, and it is still physically very complex to build a quantum computer with many qubits. However, mathematical methods can already be used to explore what fault-tolerant quantum computers could achieve in the future.
“There are a lot of myths about it, and sometimes a certain amount of hot air and hype. But we have approached the issue rigorously, using mathematical methods, and delivered solid results on the subject. Above all, we have clarified in what sense there can be any advantages at all,” says Prof. Dr. Jens Eisert, who heads a joint research group at Freie Universität Berlin and Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin.
The traveling salesman’s problem is a classic in mathematics. A traveller is to visit N cities by the shortest route and return to the starting point. As the number N increases, the number of possible routes explodes. This problem can then be solved using approximation methods. Quantum computers could provide significantly better solutions more quickly. Credit: HZB
Addressing Complex Problems
The well-known problem of the traveling salesman serves as a prime example: A traveler has to visit a number of cities and then return to his hometown. Which is the shortest route? Although this problem is easy to understand, it becomes increasingly complex as the number of cities increases and computation time explodes.
The traveling salesman problem stands for a group of optimization problems that are of enormous economic importance, whether they involve railway networks, logistics, or resource optimization. Good enough solutions can be found using approximation methods.
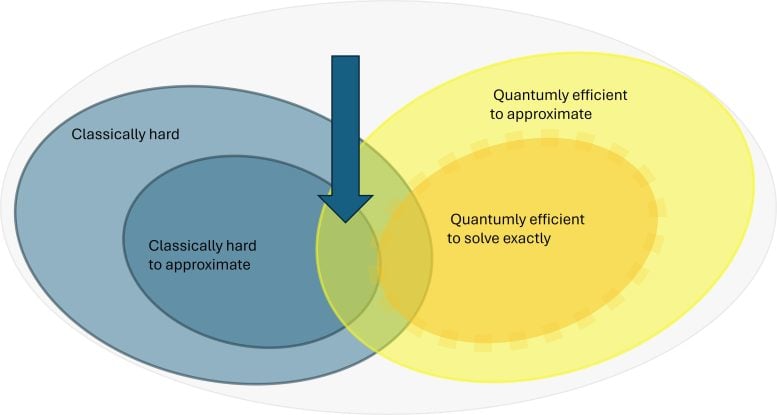
The present work (arrow) shows that a certain part of the combinatorial problems can be solved much better with quantum computers, possibly even exactly. Credit: HZB/Eisert
Quantum Solutions and Advancements
The team led by Jens Eisert and his colleague Jean-Pierre Seifert has now used purely analytical methods to evaluate how a quantum computer with qubits could solve this class of problems. A classic thought experiment with pen and paper and a lot of expertise.
“We simply assume, regardless of the physical realization, that there are enough qubits and look at the possibilities of performing computing operations with them,” explains Vincent Ulitzsch, a PhD student at the Technical University of Berlin. In doing so, they unveiled similarities to a well-known problem in cryptography, i.e. the encryption of data. “We realized that we could use the Shor algorithm to solve a subclass of these optimization problems,” says Ulitzsch.
This means that the computing time no longer “explodes” with the number of cities (exponential, 2N), but only increases polynomially, i.e. with Nx, where x is a constant. The solution obtained in this way is also qualitatively much better than the approximate solution using the conventional algorithm.
“We have shown that for a specific but very important and practically relevant class of combinatorial optimization problems, quantum computers have a fundamental advantage over classical computers for certain instances of the problem,” says Eisert.
Reference: “An in-principle super-polynomial quantum advantage for approximating combinatorial optimization problems via computational learning theory” by Niklas Pirnay, Vincent Ulitzsch, Frederik Wilde, Jens Eisert and Jean-Pierre Seifert, 15 March 2024, Science Advances.
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adj5170





